SATA
Included In This Lesson
Study Tools For SATA
Outline
UPDATE: 12/14/2017
NCSBN now allows for ONE, SOME, or ALL SATA questions to be correct. Read more here: https://www.ncsbn.org/9010.htm
Transcript
So, the first strategy we’re gonna talk about here and possibly one of the most important ones for you to understand is that of SATA questions or Select All That Applied. So, a lot of times, you’re gonna hear people will refer to these as SATA questions. And that means, it’s really those questions that you get where, you know, it’s saying, of all these options, which ones would you select? So, you’ll have anywhere from 4 to 6 or possibly even more answer options. And what you have to do is you have to select which ones are the correct answers, okay. So, these are generally every nursing students least favorite kind of NCLEX question. But as we talked about before, it’s really important to understand these because according to Bloom’s Taxonomy, these are generally those application questions. These are generally the more difficult questions and these are generally the ones, where you know, if you’re getting a lot of these, you’re probably doing pretty well because a lot of students struggle with these.
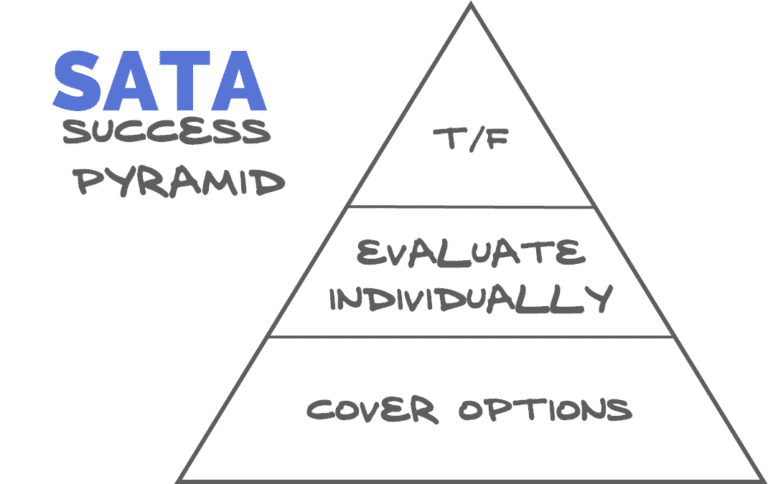
So, let’s talk about how you can do better with these kinds of questions. Now, I wanna give to you guys what I call the SATA Success Pyramid and there’s 3 levels to this pyramid. There’s 3 things that you need to do in order to find success with SATA kinds of questions. The first thing that I want you to do when you’re presented with one of these questions is I want you to cover all the options. Whether there’s 4 options or 6 options, 8 options, it doesn’t matter. Cover all the options and read the question. Okay, then what you need to do is I want you to evaluate each question or each option individually, okay. Don’t try to bunch them all together. That’s where a lot of students struggle is they say, “Okay, A is right, but A is kinda like B. So A and B must be right ‘cause they kinda always go together.” Never do that. I want you to evaluate each one individually to determine if it’s correct or incorrect. Then, what I want you to do is I want you to turn the question into a True/False statement. Okay, and then answer each, use each option, determine if each option is true and not true false statement. Alright, let’s do an example of this really quick. So, this is what I call a SATA success pyramid. I want you to apply these 3 pillars or these 3 levels of this pyramid to every select all that applied question that you get. Now, while we talk about how strategies are helpful and stuff but knowledge is king. With SATA questions, I want you to always use this strategy because these are the most difficult kinds of questions you’re gonna get. It’s very easy to get yourself running down dungeons or going in directions that you shouldn’t be going and this pyramid, this paradigm for working through these questions is really gonna help keep you on track and keep you doing exactly what you need to do to answer these questions appropriately.
So, let’s do an example and we’ll kinda walk through this. So, the question is, A nurse is caring for a patient who was admitted to the hospital for dehydration. The provider has ordered laboratory testing of blood values. Which of the following lab results would the nurse most likely see in a dehydrated patient? Select all that applied. Alright, so, we read the question, now, let’s follow the steps. That’s the first step we need to do. The first thing we need to do is we need to cover all the options, okay, because we don’t wanna start running down different rabbit holes trying to determine if different options go together. So, we’ve covered all the options, then we’re going to read just the first one and evaluate each option individually. But before we do that, we need to reword the question as a True False statement. So, you can see we went from that huge question and all we really need to do is just determine what exactly is being asked here. So, what we’re being asked, is we’re saying, in a patient that has dehydration, what lab results are we gonna see in this dehydrated patient? Okay, so we have a dehydrated patient. What lab results are we gonna see in a dehydrated patient? Select all that applied. So, in order to word that as a True False statement, all we need to say is, “True or False: a dehydrated patient will experience…blank.” So, to do the first one, true or false? A dehydrated patient will experienced increased hematocrit. Alright, so, if we go back to our Anat and Phys, we go back to some of our basic nursing sciences, if we’re losing more plasma, we’re losing more fluid, okay. We’re in this dehydrated state, are we gonna see an elevated hematocrit? So, will the percentage of red blood cells be higher in our blood if we’re losing some of our fluid, alright? That’s all we’re really asking. So, we’ve lost our fluid, is the percentage of red blood cells higher in that state? Well, we know that that is true statement. So, then what we do is we go in and we do the next one. So, true or false? A dehydrated patient will experience elevated BUN. Again, going back to our basic renal anatomy, going back to the functions of our kidneys, in our liver and our kidneys to breakdown proteins and everything. If we have a lower fluid, okay, the amount of this urea, the amount of this byproduct of protein metabolism is going to be higher in relation to the amount of fluid that we have. So, yes, we’re going to see elevated BUN. Alright, so we just keep doing this, we just keep working through this. True of false, a dehydrated patients will experience decreased sodium levels. So, in a sample of blood, alright, if we have less fluid in there, will our sodium levels also decrease in relation to that fluid? Okay, well, we know that’s not true. And again, we’re not evaluating these with each other. We say, well we had elevated BUN, so we also gonna have decreased sodium. No, it doesn’t matter, we’re not reading these together or evaluating each option individually. So, then, we read through it again, finish up the question, increased creatinine levels, doing the same thing, okay. And then, we also, you know, again, for the last one, decreased glucose levels. So, this is really kind of an easier one but obviously you knowing what we know of Anatomy and Physiology, working through the question individually, evaluating each option individually, setting it as a true false statement allows us to really answer this question. And of course, patient who’s dehydrated has decreased amounts of fluid in their blood stream and may likely have alterations in laboratory values. The patient may demonstrate increased amount of hematocrit from concentrated blood, elevated BUN and creatinine, if kidneys are not well perfused, an elevated glucose can lead to dehydration and dehydration can further elevate glucose levels. So, just working through our basic Anat and Phys, working through what we understand about the patient, we can answer this question. But using this strategy, using this pyramid for answering this is really the best way to work through this, you know. Covering all your options first when you start out, and then, evaluating each option individually, and setting it as a true false statement. That’s what I want you to really do every time you see a SATA question, is think through this, the 3 things you need to do, SATA success pyramid, and you’re gonna have much greater success on these types of questions, select all that applied questions, then, you would have otherwise. Alright guys, now, good luck!
NCLEX Review
Concepts Covered:
- Noninfectious Respiratory Disorder
- Test Taking Strategies
- Respiratory Disorders
- EENT Disorders
- Prenatal Concepts
- Studying
- Prefixes
- Suffixes
- Acute & Chronic Renal Disorders
- Disorders of the Adrenal Gland
- Integumentary Disorders
- Oncology Disorders
- Preoperative Nursing
- Musculoskeletal Trauma
- Bipolar Disorders
- Disorders of the Posterior Pituitary Gland
- Hematologic Disorders
- Community Health Overview
- Immunological Disorders
- Renal Disorders
- Childhood Growth and Development
- Labor Complications
- Upper GI Disorders
- Medication Administration
- Neurological Emergencies
- Adulthood Growth and Development
- Disorders of Pancreas
- Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Cardiac Disorders
- Disorders of the Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands
- Integumentary Important Points
- Pregnancy Risks
- Urinary Disorders
- Vascular Disorders
- Eating Disorders
- Learning Pharmacology
- Anxiety Disorders
- Basics of NCLEX
- Factors Influencing Community Health
- Lower GI Disorders
- Intraoperative Nursing
- Integumentary Disorders
- Neurologic and Cognitive Disorders
- Trauma-Stress Disorders
- Central Nervous System Disorders – Brain
- Somatoform Disorders
- Dosage Calculations
- Depressive Disorders
- Personality Disorders
- Cognitive Disorders
- Substance Abuse Disorders
- Psychological Emergencies
- Circulatory System
- Postoperative Nursing
- Hematologic Disorders
- Liver & Gallbladder Disorders
- Infectious Respiratory Disorder
- Central Nervous System Disorders – Spinal Cord
- Emergency Care of the Cardiac Patient
- Concepts of Population Health
- Peripheral Nervous System Disorders
- Note Taking
- Female Reproductive Disorders
- Oncologic Disorders
- Postpartum Complications
- Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders
- Fetal Development
- Shock
- Emergency Care of the Neurological Patient
- Respiratory Emergencies
- Labor and Delivery
- Gastrointestinal Disorders
- EENT Disorders
- Postpartum Care
- Cardiovascular Disorders
- Newborn Care
- Renal and Urinary Disorders
- Newborn Complications
- Urinary System
- Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Infectious Disease Disorders
- Nervous System
- Psychotic Disorders

