Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in Nursing
Included In This Lesson
Study Tools For Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in Nursing
Outline
Overview of Maslow’s Hierarchy
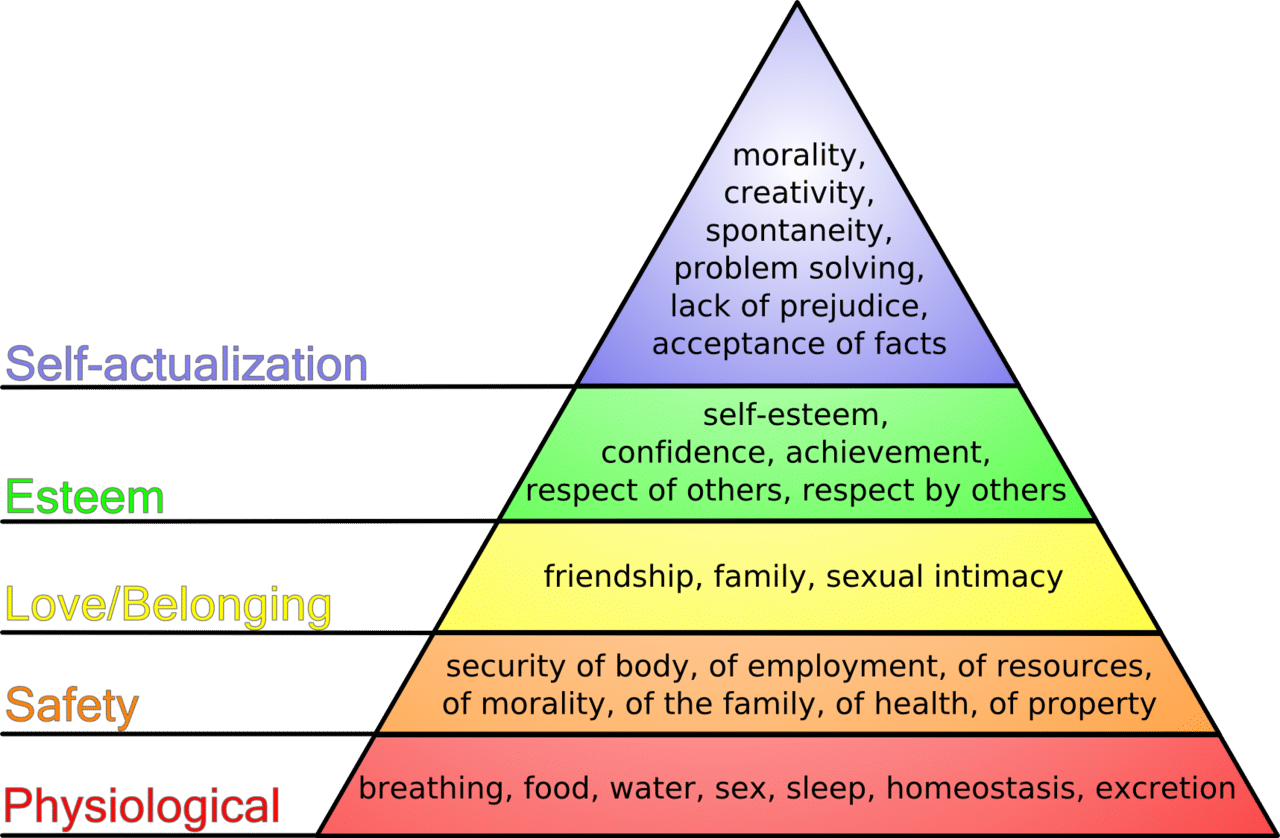
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a fundamental psychological framework that provides insights into human motivation and behavior. In the context of nursing care, it serves as a vital tool for understanding and prioritizing patients’ needs. This model is structured into five tiers, known as Maslow’s hierarchy of Needs Pyramid, each representing a distinct set of human requirements:
- Physiological Needs
- Safety Needs
- Love/Belonging Needs
- Esteem Needs
- Self-Actualization Needs
This lesson exploration dives into Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, its relevance in nursing care, and how it informs the prioritization of patient care.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: An Overview
What is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs?
Developed by Abraham Maslow, this psychological theory is rooted in the concept of human needs. It posits that individuals are driven by a hierarchy of needs, with basic physiological needs at the foundation and higher-level self-actualization needs at the pinnacle.
Understanding Maslow’s hierarchy is crucial for healthcare professionals, particularly nurses, as it forms the basis for effectively identifying and addressing patients’ needs.
The Five Levels of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Physiological Needs
At the bottom of the pyramid, you’ll see physiological needs, which take precedence over all other requirements. These encompass fundamental elements essential for human survival, such as oxygen, fluids, nutrition, shelter, and elimination. In a healthcare context, ensuring that patients’ physiological needs are met is the highest priority, as these are the building blocks of overall well-being.
Safety Needs
The next level of prioritization involves safety and security needs. These needs encompass both physical and psychological safety. Patients should feel physically safe in their environment, free from harm or danger. Psychological safety is equally vital, as individuals often seek safety before addressing any other needs. This level includes concepts like law and order, shelter, employment, and health security.
Love/Belonging Needs
The third tier pertains to the need for social relationships and a sense of belonging. It involves the desire for acceptance and connection with others. Examples of these needs include relationships with family members, friendships, social connections, and intimate relationships. Addressing these needs is essential for promoting emotional well-being.
Esteem Needs
As patients progress up the hierarchy, esteem needs become more significant. These needs encompass the desire for outer acceptance, recognition, status, respect, and the need to feel useful. They are particularly relevant once the lower-level needs are adequately met. Fulfilling esteem needs promotes a sense of self-worth, confidence, and accomplishment.
Self-Actualization Needs
At the pinnacle of Maslow’s Hierarchy are self-actualization needs, which can only be fully realized once all other needs have been satisfied. Self-actualization involves reaching one’s full potential, focusing on personal growth, creativity, and problem-solving capabilities. Encouraging individuals to be their best selves and pursue their unique talents and aspirations aligns with self-actualization needs.
The Relevance of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in Nursing Care
Nursing care is fundamentally centered around addressing patients’ needs, making Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs an invaluable framework for guiding healthcare professionals. By understanding and applying this model, nurses can provide more effective and patient-centric care.
Prioritization
One of the key applications of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in nursing care is prioritization. When caring for patients with diverse needs, nurses must determine which needs require immediate attention. Physiological needs take precedence over all others, ensuring patients have access to oxygen, fluids, nutrition, shelter, and appropriate elimination processes.
For instance, if a patient becomes breathless during a conversation, indicating a potential oxygen deficiency, the nurse should halt the conversation and prioritize assessing and addressing the patient’s oxygen levels. This immediate action aligns with the model’s emphasis on physiological needs as the highest priority.
Nursing Points
Nurses must consider several crucial points when applying Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in practice:
General Understanding
Nurses should have a comprehensive understanding of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs to effectively prioritize patient care and tailor interventions accordingly.
Physiological Needs
Meeting physiological needs is the foundation of nursing care. It involves ensuring patients have access to essential elements like oxygen, fluids, nutrition, shelter, and appropriate elimination processes.
Safety Needs
Patients must feel safe in their healthcare environment. Nurses should promote physical safety by preventing accidents and maintaining order. Moreover, addressing psychological safety concerns, such as emotional support, is vital.
Love and Belonging Needs
Building rapport with patients is essential for addressing their love and belonging needs. Nurses should encourage healthy social relationships and family support whenever possible.
Self-Esteem Needs
Patients’ self-esteem needs should be addressed through therapy and encouragement of personal growth. Recognizing achievements, respecting individual status, and fostering self-confidence are integral aspects of nursing care.
Self-Actualization Needs
While self-actualization is the highest level of need, nurses can still contribute to this aspect by focusing on long-term goals and supporting patients’ rehabilitation and return to their homes.
Putting Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs into Nursing Practice
In the dynamic world of nursing care, the application of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs can be instrumental in delivering efficient and patient-centric services.
Prioritizing Care for Multiple Patients
Nurses frequently encounter situations where they must prioritize care among multiple patients. Maslow’s model provides a clear framework for making these decisions. In such scenarios, physiological needs should always take precedence over self-actualization needs. Ensuring that patients’ basic requirements are met is paramount.
Meeting Unmet Needs
Many patients arrive at healthcare facilities with unmet needs. Nurses play a vital role in identifying and addressing these needs through comprehensive assessments. Prioritizing needs in categorical order, starting with physiological needs and proceeding to safety, love, esteem, and self-actualization, guides effective care delivery.
Nursing Concepts Supported by Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Several fundamental nursing concepts align with Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs:
Prioritization
Prioritizing patient care based on the hierarchy of needs is a cornerstone of nursing practice. It ensures that the most critical needs receive immediate attention, thereby enhancing patient outcomes.
Clinical Judgment
The application of clinical judgment is closely tied to prioritization. Nurses must assess patient conditions and make informed decisions about which needs to be addressed first.
Patient Education
Nurses can utilize the hierarchy to educate patients about their own needs. For example, if a patient wishes to engage in a lengthy conversation but experiences a decrease in oxygen saturation, the nurse can emphasize the importance of pausing the conversation to improve oxygen levels. This educational approach aligns with prioritizing higher-priority needs over others.
Linchpins For Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
In conclusion, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a foundational framework in nursing care. It guides nurses in prioritizing and addressing patients’ needs effectively, ensuring that basic physiological requirements are met before addressing higher-level needs.
Here are some key reasons why Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs pyramid holds such significance:
Comprehensive Understanding of Human Needs: The pyramid offers a structured insight into the hierarchy of human needs, ranging from basic physiological requirements to higher-order aspirations. This comprehensive understanding allows professionals in diverse fields to tailor their approaches to meet individuals’ specific needs effectively.
Prioritization: In fields like healthcare, education, and emergency services, prioritization is crucial. Maslow’s model provides a clear roadmap for prioritizing needs, ensuring that the most critical ones receive immediate attention. This prioritization can save lives, enhance well-being, and improve outcomes.
Holistic Approach: By recognizing that human needs encompass not only physical but also psychological and emotional aspects, Maslow’s model promotes a holistic approach to care and management. It encourages professionals to consider the whole person, addressing not just immediate concerns but also long-term growth and self-fulfillment.
Enhanced Decision-Making: In leadership and management, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs assists in decision-making. Understanding what motivates individuals at different levels of the hierarchy helps leaders create more effective strategies for employee engagement, customer satisfaction, and organizational success.
Personal Growth and Development: Beyond professional applications, the pyramid serves as a powerful tool for personal growth and self-awareness. Individuals can use it to identify where they currently stand in terms of their own needs and aspirations, helping them set meaningful goals and work towards self-actualization.
Crisis Intervention: In times of crisis, such as natural disasters or public health emergencies, Maslow’s model guides emergency responders and relief organizations in providing immediate relief while considering the long-term needs of affected individuals and communities.
Educational Framework: In education, the model informs teaching and curriculum design by recognizing that students’ ability to learn and thrive is influenced by their unmet needs. Educators can tailor their approaches to create a supportive and conducive learning environment.
Psychological Insights: Psychologists and therapists use Maslow’s model to understand the root causes of individuals’ psychological struggles. It helps in uncovering unmet needs and developing therapeutic strategies that address these underlying issues.
Motivation and Productivity: In the workplace, understanding where employees fall within the hierarchy can boost motivation and productivity. Recognizing that higher-level needs, such as esteem and self-actualization, play a role in job satisfaction can lead to more engaged and fulfilled employees.
By understanding and applying Maslow’s hierarchy needs pyramid, nurses can provide holistic and patient-centric care that enhances overall well-being and outcomes. In essence, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs pyramid serves as a universal framework that underscores the intrinsic connection between human well-being and the fulfillment of fundamental needs.
Transcript
All right. We’re going to talk about Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Now, this is something that’s really important, but I feel like is often glossed over in nursing school, or we don’t understand exactly how to use it or how important it is.
First of all, what is the hierarchy of needs? Well, this was developed by Abraham Maslow. It’s really a psychological theory based on our human needs. It’s based on the priority of our human needs. So not just what we need as human but in what order we need those things. First of all, it focuses on physiological needs. Then it’s going to focus on safety, love belonging, esteem and self-actualization.
We’re going to dive into this a bit more. But each of these builds on each other. We don’t worry about love and belonging until safety is met. We don’t worry about self-esteem until our physiological needs are met. What are the physiological needs that we have? Now, these take priority before anything else. Remember, this is the very bottom of that pyramid. These are the most important things that we must have met before anything else. Examples of these would be oxygenation. We have to be able to breathe. Things like fluids and nutrition, shelter, and the ability to eliminate.
These things must happen before anything else. The best way to think of this is with our ABCs, our airway, breathing, circulation. Until our ABCs are met we don’t worry about anything else. We focus on our As before our Bs, focus on our Bs before our Cs. This is the very bottom of our pyramid in Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Now, the next one is safety. Once our physiological needs are met, once our ABCs are met, we can then start looking at safety. This is the second level need. We have down here our physiological needs. Right above that is safety. Okay. Once all of our physiological needs are met we can start focusing on our patient’s safety.
Now, there’s psychological safety where people attempt to seek safety before meeting any other needs. For example, when a patient’s in the hospital, they’re going to want to be sure that their home is safe. They want to make sure that they’re safe in the hospital. Examples of this would be like law and order, shelter, employment, and health. They want to make sure all those psychological safety needs are met. Then, we also have physical safety. Patients need to feel physically safe. Now, with this we have infection, biological safety and then we also have physical environmental safety. That’s going to be lights, extension cords, things like that with our patients who maybe have dementia. Then, we also want to have our bed rails up and all those types of things. So we have our physical safety and our psychological safety.
The next one we’re going to focus on in our third level of our pyramid once we have our safety met, is we can focus on our love and belonging needs. This is our third level. Now, all of our patients have a need for social relationships. They need to feel connected to other humans. Now, some examples of this would be like relationship with family members. It might be friendships. It might be social relationships. It might be intimate relationships. As a nurse, we can also sit there, talk with our patients, give them that social connection, give them that sense of love and belonging.
Then there’s esteem. It’s the fourth level need. Now, this becomes very important once all of our other needs are met, once our physiological needs are met, our safety needs are met, our love and belonging. Then we can start worrying about esteem. Okay. We focus on outer esteem first then we focus on … our outer acceptance first and then we focus on esteem. First, focus on being accepted then focus on building up esteem. Patients want to feel useful. They have a need for feeling of accomplishment or a need for self-confidence and self-worth. Some examples of this might be they need to have recognition. They need to feel status. They need to feel respect. As a nurse, some things we can do is recognize our patients when they do make accomplishments or when they are working harder, when they are progressing. It’s really important that people feel this.
Then our next level need, our fifth level need is going to be self-actualization. We must meet this need once every other need has been met. People want to feel like they’ve actualized their full potential, or they’ve achieved their full self. We can focus on coping here. We can encourage problem solving capabilities. This is really kind of like being your best self. This is when we’ve achieved that sense of being our best self. Some examples of ways that this can happen is we can be pursuing talents. We can be pursuing personal growth. We have the ability to be creative.
Now, Maslow’s and nursing. How does this all apply to nursing? Nurses really need to prioritize the care of their patients based on this model. We must meet the physiological needs of our patients before we do anything else. If we’re talking to a patient, and a patient becomes winded we need to stop the conversation. That’s a love and belonging need where we really need to start focusing on their O2 status, which is a physiological need. O2 comes before love and belonging. We must encourage safety needs. We must make sure the patient’s room is safe. We must encourage the patient to engage in safe behavior also.
Then love and belonging, we can build rapport. We can go in there and introduce ourselves, encourage family support if the patient has family support or encourage friend support as long as that is healthy and a positive influence on the patient. Of course, there’s going to be situations where we might not want the family there because they’re not a positive influence on our patient. Then we can start meeting self-esteem needs. We meet this through therapy, through encouraging success, through recognizing successes that the patient’s having. Then we can start looking at self-actualization needs. We can start looking at long-term goals. This is where we start getting into those planning phases with our patient of where are we going to be? What’s our long long-term goals for recovery? We can start looking at rehabilitation and returning to home.
I really want you, as you’re working as a nurse and as you’re practicing as a nurse and you’re on a floor, really think about this pyramid. Don’t just see this as something that you must memorize for a test. But really think about this pyramid and especially focus on these first couple rungs right here, that we’re meeting these physiological needs of our patient, we’re meeting the safety needs of our patient. Then we can start dealing with these other issues and these other things. In our test-taking course we do talk about this as well and how to answer questions on tests and how to prioritize care. We’re going to talk about this more and more as we go on in this fundamentals course.
How do you prioritize the care of multiple patients? You can use Maslow’s hierarchy of needs to determine which patient should come first. Physiological needs come before self-actualization needs. If you have a patient who has an ABC need, you deal with that first before you deal with a patient who maybe has an education need. You even deal with an ABC need before you deal with a safety need. This is how you can prioritize care and put this Maslow’s hierarchy of needs into practice in your nursing care. You must meet your patient’s needs. Patients often come to the hospital with many, many, many unmet needs. We need to identify those needs through our assessment.
That’s the whole importance of doing a holistic and a complete assessment on our patient is we can start to identify, okay, yeah, the ABCs are all met. The patient’s safe. Now we can start looking at these other ones, love and belonging, esteem, self-actualization. We can start looking at these other needs and start addressing those in order, making sure that, boom, that’s all taken care of. That’s all taken care of, and start really working up this pyramid to make sure that the patient’s needs are first. Again, addressing our physiological needs first, then safety, then love. That’s really the importance of our assessment. And then categorizing our patient’s needs and prioritizing our care as such.
Now, some of the nursing concepts you’re going to see with this are prioritization, of course. We’ve got to prioritize our patient’s care and we’ve got to prioritize our patients as we’re taking care of multiple patients. Then, clinical judgment would be another nursing concept you’re going to see here because this really comes into play on how you use your judgment and your critical thinking in nursing care.
Let’s talk really quick to wrap up on the key points of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. There’s five levels in Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. There is a cheat sheet on this and there’s other resources on this. But the first one is physiological needs. We must meet those ABCs of our patient before we address anything else. Then we can really focus on safety. Encourage a safe environment and safe habits and safe practices by our patient. Make sure there’s a culture of safety. Make sure they understand how to be safe. Make sure that they understand things that they can adjust in their lives to continue to be safe.
Then we can focus on love and belonging. Reinforce the building and maintenance of strong social relationships. Then we can focus on esteem, where we encourage our patient, we reinforce with our patient and we help our patient feel that esteem. Then there’s self-actualization. We help the patient set goals and we help them along that path of both short-term and long-term goals.
All right, guys. That’s the basics of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Make sure you check out all the other resources, the quiz questions, the cheat sheets that go along with this lesson. Now go out and be your best selves today. As always, happy nursing.
Monalisa’s Study Plan
Concepts Covered:
- Community Health Overview
- Circulatory System
- Urinary System
- Communication
- Prenatal Concepts
- Test Taking Strategies
- Respiratory Disorders
- EENT Disorders
- Developmental Theories
- Legal and Ethical Issues
- Prefixes
- Suffixes
- Acute & Chronic Renal Disorders
- Disorders of the Adrenal Gland
- Preoperative Nursing
- Integumentary Disorders
- Integumentary Disorders
- Prioritization
- Bipolar Disorders
- Disorders of the Posterior Pituitary Gland
- Hematologic Disorders
- Immunological Disorders
- Renal Disorders
- Childhood Growth and Development
- Labor Complications
- Upper GI Disorders
- Medication Administration
- Developmental Considerations
- Adulthood Growth and Development
- Disorders of Pancreas
- Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Musculoskeletal Trauma
- Disorders of the Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands
- Integumentary Important Points
- Pregnancy Risks
- Urinary Disorders
- Cardiac Disorders
- Learning Pharmacology
- Documentation and Communication
- Anxiety Disorders
- Basic
- Factors Influencing Community Health
- Prenatal and Neonatal Growth and Development
- Lower GI Disorders
- Eating Disorders
- Trauma-Stress Disorders
- Microbiology
- Oncology Disorders
- Somatoform Disorders
- Fundamentals of Emergency Nursing
- Dosage Calculations
- Concepts of Population Health
- Understanding Society
- Depressive Disorders
- Personality Disorders
- Cognitive Disorders
- Substance Abuse Disorders
- Psychological Emergencies
- Hematologic Disorders
- Liver & Gallbladder Disorders
- Emergency Care of the Cardiac Patient
- Female Reproductive Disorders
- Delegation
- Vascular Disorders
- Oncologic Disorders
- Postpartum Complications
- Fetal Development
- Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders
- Basics of NCLEX
- Shock
- Studying
- Concepts of Mental Health
- Labor and Delivery
- Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Health & Stress
- Neurological Emergencies
- EENT Disorders
- Emotions and Motivation
- Intraoperative Nursing
- Digestive System
- Central Nervous System Disorders – Brain
- Tissues and Glands
- Postpartum Care
- Cardiovascular Disorders
- Newborn Care
- Renal and Urinary Disorders
- Newborn Complications
- Neurologic and Cognitive Disorders
- Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Infectious Disease Disorders
- Nervous System
- Respiratory System
- Behavior
- Terminology
- Respiratory Emergencies
- Peripheral Nervous System Disorders
- Proteins
- Noninfectious Respiratory Disorder
- Basics of Human Biology
- Neurological Trauma
- Concepts of Pharmacology
- Statistics
- Emergency Care of the Neurological Patient
- Basics of Sociology
- Central Nervous System Disorders – Spinal Cord
- Infectious Respiratory Disorder
- Psychotic Disorders
- Emergency Care of the Trauma Patient

