Nursing Care Plan (NCP) for Skin cancer – Melanoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Included In This Lesson
Study Tools For Nursing Care Plan (NCP) for Skin cancer – Melanoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Outline
Lesson Objectives for Skin Cancer (Melanoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma)
- Understanding Skin Cancer Types:
- Define and differentiate between melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma, including their distinctive characteristics, risk factors, and cellular origins.
- Risk Factors and Prevention:
- Identify common risk factors associated with each type of skin cancer.
- Explore preventive measures, including sun protection strategies, regular skin examinations, and early detection practices.
- Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis:
- Recognize the clinical manifestations of melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
- Understand the diagnostic methods used to confirm the presence of skin cancer, such as biopsies, imaging studies, and staging procedures.
- Treatment Modalities:
- Explore the various treatment modalities for skin cancer, including surgical interventions, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies.
- Understand the goals of each treatment option and potential side effects.
- Patient Education and Support:
- Emphasize the importance of patient education on skin cancer prevention, self-examination, and adherence to treatment plans.
- Explore strategies for providing emotional support to individuals diagnosed with skin cancer and their families.
Pathophysiology of Skin Cancer (Melanoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma)
Melanoma:
- Abnormal Melanocyte Growth:
- Melanoma arises from the uncontrolled growth of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in the skin.
- Mutations in melanocytes result in the formation of malignant melanoma cells.
- Invasion and Metastasis:
- Melanoma cells have the ability to invade surrounding tissues and metastasize to other parts of the body.
- Early detection is crucial to prevent the spread of melanoma to distant organs.
- Immune System Response:
- The immune system plays a role in recognizing and eliminating abnormal cells, including melanoma cells.
- Immune evasion mechanisms by melanoma cells can contribute to tumor progression.
Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
- Epidermal Cell Abnormalities:
- Basal cell carcinoma arises from the basal cells of the epidermis, while squamous cell carcinoma originates from the squamous cells.
- Both involve the abnormal growth and proliferation of these epidermal cells.
- Cumulative UV Radiation Damage:
- Chronic exposure to UV radiation, primarily from sunlight, is a major contributor to the development of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
- UV radiation induces DNA damage, leading to mutations in skin cells.
- Local Invasion:
- Basal cell carcinoma tends to invade locally into surrounding tissues but has a lower potential for metastasis.
Squamous cell carcinoma may invade locally and has a higher risk of metastasis, especially in advanced stages.
- Immunosuppression Influence:
- Immunosuppression, whether due to medical conditions or medications, can increase the risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma.
- Individuals with weakened immune systems may have reduced ability to control abnormal cell growth.
- Precancerous Lesions:
- Actinic keratosis, a precancerous skin lesion, can progress to squamous cell carcinoma.
- Identification and treatment of precancerous lesions are important in preventing the development of squamous cell carcinoma.
Etiology of Skin Cancer (Melanoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma)
Melanoma:
- UV Radiation Exposure:
- Prolonged exposure to UV radiation, whether from sunlight or tanning beds, is a primary environmental factor.
- Intense, intermittent exposure and sunburns increase the risk of melanoma.
- Fair Skin and Eye Color:
- Individuals with fair skin, light-colored eyes, and light hair are at a higher risk due to lower melanin levels, which provide less natural protection against UV radiation.
- Family History
- Genetic factors contribute to melanoma risk, especially in individuals with a family history of the disease.
- Specific genetic mutations, such as mutations in the CDKN2A gene, are associated with an increased risk.
- Immunosuppression:
- Weakened immune systems, either due to medical conditions or medications, can increase the susceptibility to melanoma.
- Immunocompromised individuals may have difficulty controlling abnormal cell growth.
- Presence of Atypical Moles:
- Individuals with atypical moles (dysplastic nevi) have an increased risk of developing melanoma.
- Regular monitoring and early removal of atypical moles are important preventive measures.
Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
- UV Radiation Exposure:
- Cumulative exposure to UV radiation is the primary environmental risk factor for both basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
- Chronic sun exposure over many years increases the likelihood of DNA damage.
- Fair Skin and Eye Color:
- Individuals with fair skin, light-colored eyes, and light hair are at higher risk due to reduced melanin levels.
- Darker skin provides some natural protection against UV radiation.
- Age and Cumulative Sun Exposure:
- Older individuals with a history of prolonged sun exposure over their lifetime are at an increased risk.
- Cumulative damage from UV radiation contributes to the development of skin cancers.
- Immunosuppression:
- Weakened immune systems, whether from medical conditions or medications, increase the risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma, particularly in organ transplant recipients.
- Presence of Precancerous Lesions:
- Actinic keratosis, characterized by scaly or crusty skin patches, is a precursor to squamous cell carcinoma.
- Identifying and treating actinic keratosis can reduce the risk of progression to squamous cell carcinoma.
Desired Outcome in the Management of Skin Cancer (Melanoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma)
- Early Detection and Treatment:
- Achieve early detection and prompt treatment of skin cancer lesions to prevent progression and improve outcomes.
- Increase awareness and encourage regular skin self-examinations.
- Complete Lesion Removal:
- Ensure complete removal of cancerous lesions through surgical interventions or other appropriate treatments.
- Reduce the risk of recurrence by addressing all cancerous cells during removal.
- Prevention of Recurrence:
- Minimize the risk of cancer recurrence through ongoing surveillance and preventive measures, including sun protection strategies.
- Encourage lifestyle modifications to reduce UV radiation exposure.
- Psychosocial Support:
- Provide psychosocial support to individuals diagnosed with skin cancer and their families.
- Address emotional challenges, anxiety, and concerns related to the impact of skin cancer on appearance and well-being.
- Patient Education on Surveillance:
- Educate patients on the importance of continued surveillance for new or changing skin lesions.
- Promote regular follow-up appointments for ongoing monitoring and early intervention if new lesions arise.
Subjective Data:
- Itching
- Painful bumps on the skin
Objective Data:
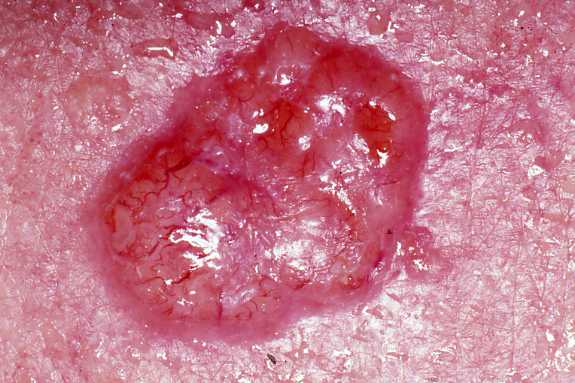
- Shiny pink, red or pearly bumps on the skin
- Skin growths with raised borders that are crusty in the center
- The white, yellow or waxy area with irregular borders (may resemble a scar)
- Open sore that does not go away (weeks)
- Raised growth with a rough surface
- Wart-like growth
- Suspicious Mole (ABCDE)
- Asymmetry
- Borders
- Color
- Diameter
- Elevation
Nursing Assessment for Skin Cancer (Melanoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma)
- Skin Examination:
- Conduct a comprehensive skin examination, including assessment of existing lesions, moles, and any areas of concern.
- Document the characteristics of lesions, such as size, color, irregular borders, and changes over time.
- Risk Assessment:
- Assess risk factors for skin cancer, including UV radiation exposure, family history, skin type, and immunosuppression.
- Identify modifiable risk factors and provide education on preventive measures.
- Lesion Documentation and Monitoring:
- Document the location, size, and characteristics of skin lesions using standardized tools.
- Monitor changes in lesions over time, including alterations in color, shape, size, or the development of symptoms.
- Psychosocial Assessment:
- Assess the emotional impact of a skin cancer diagnosis on the patient’s mental health and well-being.
- Identify coping mechanisms and provide appropriate support or referrals for counseling.
- Educational Needs:
- Assess the patient’s knowledge of skin cancer, risk factors, and preventive strategies.
- Identify educational needs and provide information on skin self-examinations, sun protection, and the importance of follow-up care.
- Treatment Adherence:
- Evaluate the patient’s adherence to recommended treatments and interventions.
- Address any barriers to adherence, provide clarification on treatment plans, and offer support.
- Pain Assessment:
- Assess pain levels, discomfort, or symptoms associated with skin cancer lesions or treatment procedures.
- Implement pain management strategies and monitor the effectiveness of interventions.
- Functional Status:
- Evaluate the impact of skin cancer on the patient’s functional status and daily activities.
- Collaborate with the healthcare team to address any limitations or challenges and enhance the patient’s quality of life.
Implementation for Skin Cancer (Melanoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma)
- Surgical Interventions:
- Coordinate and assist in surgical procedures for lesion removal, ensuring complete excision.
- Provide preoperative and postoperative care, including wound care, monitoring for complications, and pain management.
- Topical Treatments and Medications:
- Administer topical treatments or medications as prescribed for specific types of skin cancer.
- Educate patients on the proper application and potential side effects of prescribed medications.
- Education on Sun Protection:
- Conduct educational sessions on sun protection strategies, including the use of sunscreen, protective clothing, and avoiding peak sunlight hours.
- Emphasize lifestyle modifications to reduce UV radiation exposure.
- Psychosocial Support and Counseling:
- Offer psychosocial support to individuals coping with a skin cancer diagnosis.
- Facilitate counseling services or support groups to address emotional challenges and enhance coping mechanisms.
- Follow-Up Surveillance:
- Establish a regular follow-up schedule for ongoing surveillance and monitoring of the patient’s skin.
- Collaborate with healthcare providers to ensure timely evaluations and interventions for new or changing lesions.
Nursing Interventions and Rationales
| Nursing Intervention (ADPIE) | Rationale |
| Assess skin from head to toe; note areas of suspected skin cancers and their size and characteristics | Get baseline data to determine if growth continues to spread or if treatment is effective |
| Prepare patient and assist with biopsies of skin lesions (Most biopsies will be performed by punch or scalpel) | educate patient on what is being done. Help prepare any supplies or equipment needed to perform the task. |
| Assess and manage pain | patients may experience pain after a procedure. |
| Monitor for signs of infection following biopsy or excision (pus, odor, color) | after a biopsy, there may be an open wound which increases risk of infection |
| Apply/Administer Medications | more superficial basal cell carcinomas may just require topical medications whereas more advanced stage cancer like melanoma may require other medications, watch for any adverse reaction after medication given |
| Education on prevention-
Avoidance of UV exposure Wearing sunscreen, hats, long sleeves, sunglasses) Avoiding tanning beds ABCDE mnemonic |
patients can easily self-monitor themselves from home and report any suspicious changes in their skin to their doctor or a dermatologist |
Evaluation for Skin Cancer (Melanoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma)
- Completeness of Lesion Removal:
- Evaluate the success of surgical interventions in achieving complete removal of cancerous lesions.
- Monitor for any signs of recurrence or the development of new lesions in the treated area.
- Effectiveness of Topical Treatments:
- Assess the effectiveness of prescribed topical treatments or medications in controlling or eliminating skin cancer lesions.
- Monitor for improvements in lesion characteristics and the absence of adverse reactions.
- Adherence to Sun Protection Measures:
- Evaluate the patient’s adherence to sun protection strategies and lifestyle modifications.
- Assess changes in behavior and awareness regarding UV radiation exposure.
- Psychosocial Well-being:
- Assess improvements in psychosocial well-being through regular communication and feedback.
- Monitor the patient’s emotional state, coping mechanisms, and overall adjustment to life with or after skin cancer.
- Surveillance and Early Detection:
- Evaluate the effectiveness of follow-up surveillance in detecting new or changing skin lesions.
- Measure the success of early detection strategies in preventing the progression of skin cancer and improving outcomes.
References
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/basal-cell-carcinoma/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20354193
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15818-skin-cancer
Reviewed
Reviewed by: Jon Haws, RN, BSN, CCRN Alumnus
Last reviewed on: September 14, 2023
Transcript
Hey everyone, today, we’re going to be creating a nursing care plan for skin cancer. That includes melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. So if you’re ready, let’s get started. We’re going to first go over pathophysiology. So skin cancer is an uncontrolled growth of abnormal skin cells. There are three types of skin cancers: basal cell carcinoma is the most common, squamous cell carcinoma is also common, and melanoma, which is less common, is more dangerous. Nursing considerations: you want to do a full head to toe assessment, assist with skin biopsy, manage pain, monitor for signs of infection, administer medications, and educate patient on preventing skin cancer. Desired outcome: the patient will be free from skin cancer. The patient will be educated on prevention of skin cancers, and the patient will be free from complications or metastasis.
Okay, we’re going to go ahead and get started on a care plan. So we’re going to be going through some subjective data and we’re going to go through some objective data. So what are we going to see with these patients? The patient may be complaining of some itchiness or some painful bumps. You might also see shiny pink or red pearly bumps. You may also see white, yellow, or waxy spots with an irregular border. Other things to consider that you might see are some skin growth with raised borders that are crusty in the center, or an open sore that doesn’t go away. Assess a suspicious mole using the mnemonic A, B, C, D, E.
So interventions. We want to make sure we’re doing an assessment from head to toe. You want to make sure that we’re noting areas of suspected skin cancers and their size and characteristics. We want to make sure we’re getting baseline data to determine if the growth continues to spread or if the treatment is being effective. Another invention we’re going to be doing is to prepare the patient by assisting with the biopsy of the skin lesions. This is performed by a punch or scalpel. So we want to educate the patient on what is being done. We want to help prepare any supplies or equipment that’s needed and able to perform this task. Another invention we want to do, we want to make sure we’re managing pain as some patients may experience pain after a procedure. So we may want to give them some pain medication as needed. We’re going to monitor for signs of infection following a biopsy. So, odor and color after a biopsy as it may be an open wound which would increase their risk of the infection.
Another intervention we want to do is apply or administer any sort of medications.The more basal cell carcinomas usually just require a topical medication, whereas advanced stage cancers, like melanomas, may require other medications. So we want to watch for any sort of adverse reactions with any medication that is given. We also want to make sure we’re educating on prevention. This is a biggie: prevention of skin cancer. So what are we going to educate them on? We want them to avoid UV exposure, and want to make sure they’re wearing sunscreen when they are in the sun. They can also wear some hats, long sleeve shirts, and make sure they’re wearing sunglasses. They want to avoid tanning booths – huge, huge avoiding tanning beds and tanning booths. Another big thing is the pneumonic, A, B, C, D E. So patients can easily self monitor themselves from home and report any suspicious changes in their skin to their doctor or dermatologist.
Hey, we’re going to go over the key points. So skin cancer is an uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells. The main causes are tanning beds and UV radiation. Subjective and objective data: may complain of itchiness, painful bumps on the skin, shiny pink pearly bumps, skin growth with raised borders, open source that do not go away, wart-like growth, white, yellow, or waxy area with irregular borders. We want to do a full head to toe assessment. You’ll assist in skin biopsy of lesions and monitor for signs of infection post biopsy. We’ll want to make sure we’re applying or administering medications. And the big thing is education – educating the patient on preventing skin cancer. All right. And that we have a completed care plan.
You guys did amazing. We love you guys. Go out, be yourselves today and, as always, happy nursing.
Nursing Care Plans
How do I write a Nursing Care Plan? Why and how do we even use Nursing Care Plans? Sound familiar?
Our Nursing Care Plan Course will answer those questions and help you understand the most effective way to write a Nursing Care Plan including how to write a nursing diagnosis, interventions, and more. PLUS, we are going to give you examples of Nursing Care Plans for all the major body systems and some of the most common disease processes. The course also includes a nursing care plan template that you can use to quickly complete care plans. When you complete this course, you will be able to write and implement powerful and effective Nursing Care Plans.